Motivation and Problem
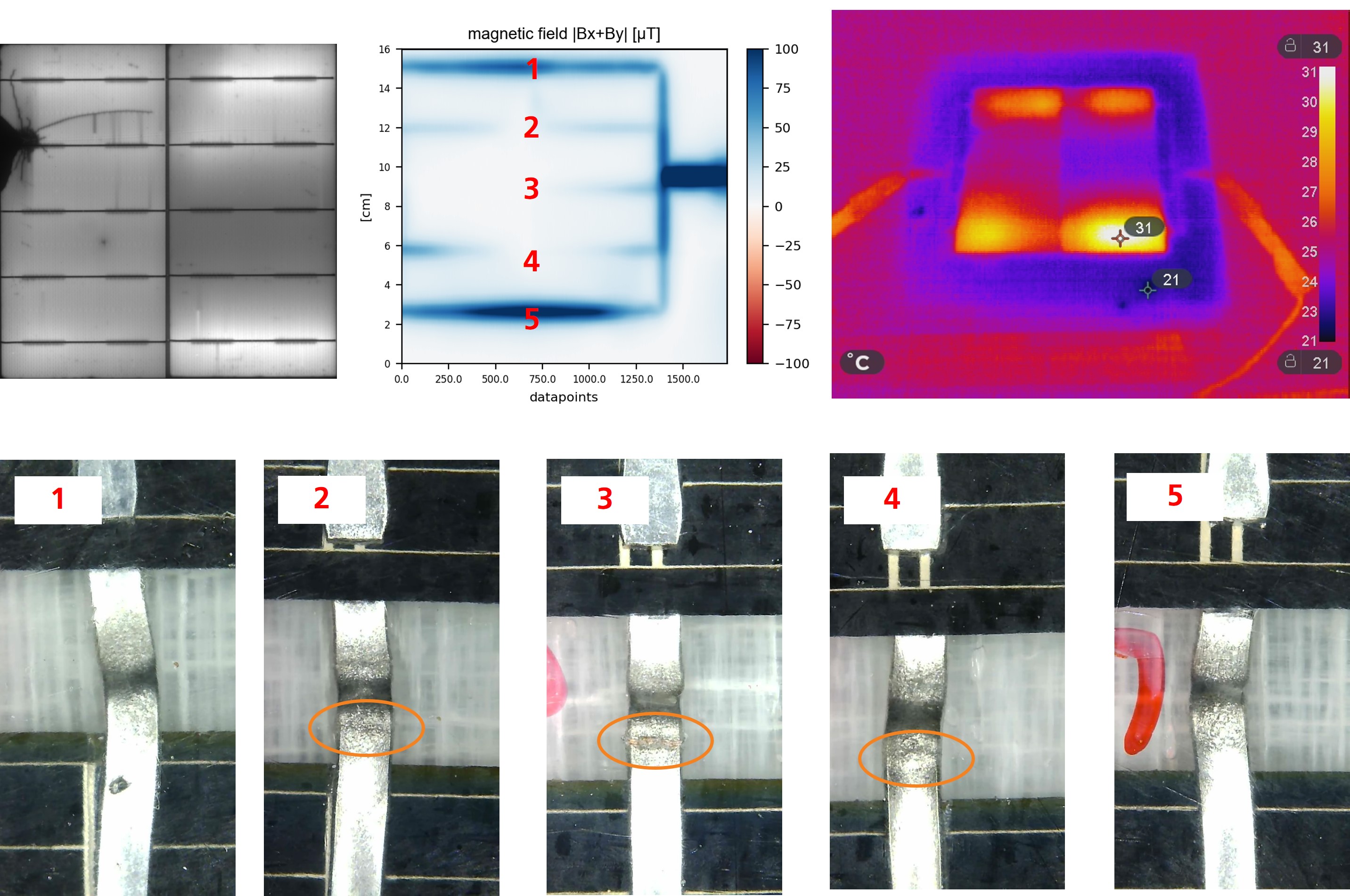
New types of photovoltaic modules are becoming increasingly complex in terms of busbars and connection points. Thinner cell connections and the switch from flat to round wires mean that previous two-dimensional simplifications in mechanical simulation are no longer acceptable, as areas of bending that were previously not taken into account are now also affected.
The reduction of heavy metals requires the substitution of lead in solder joints, making alternative lead-free solders and conductive adhesives more important. At the same time, alternative materials for lightweight modules without glass lead to increased stress on cell connections due to large differences in expansion.
Thermal-mechanical loads caused by temperature changes are an essential aspect of PV module development. Knowledge of module temperatures at different locations, depending on environmental parameters and module design, is crucial for the module's “mission profile.”
 Fraunhofer Center for Silicon Photovoltaics CSP
Fraunhofer Center for Silicon Photovoltaics CSP